Introduction to Indoor Farming
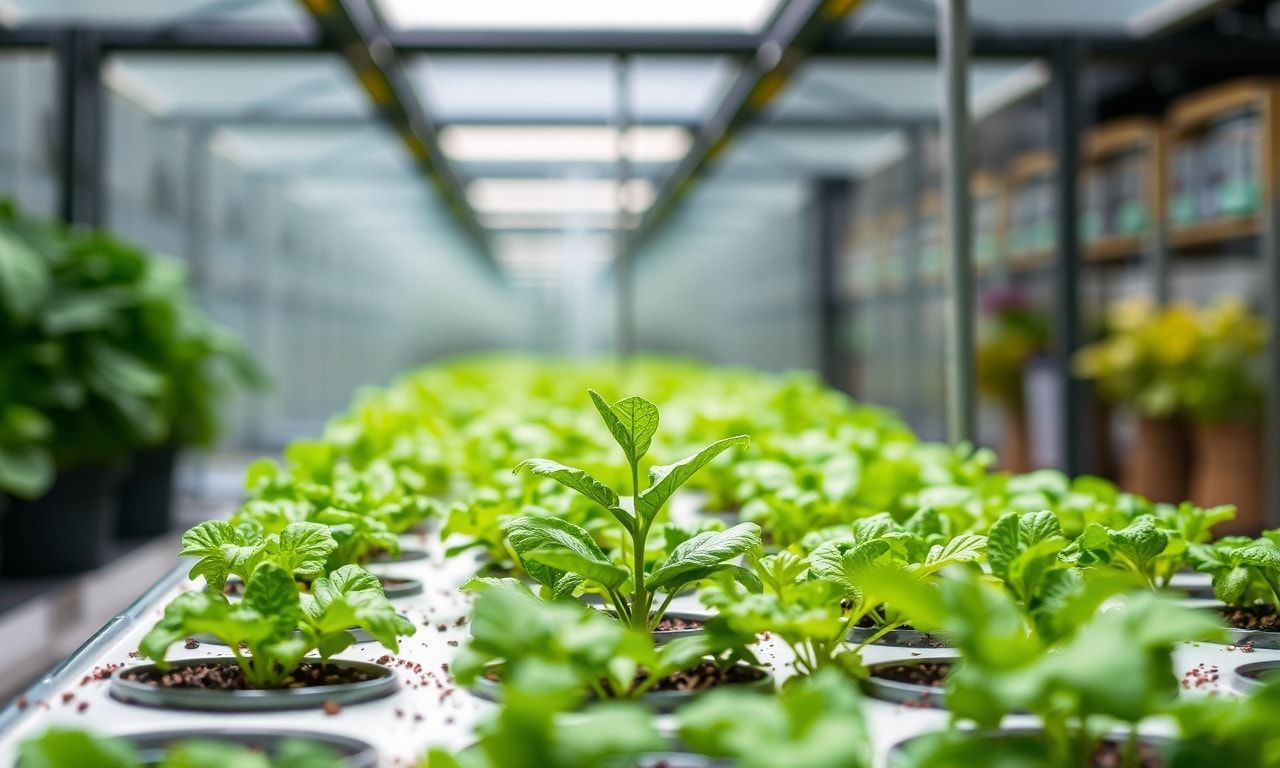
Indoor farming, also known as urban farming or vertical farming, is a revolutionary approach to agriculture that is gaining traction worldwide. This method involves growing crops in a controlled environment, often using advanced technologies such as hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics. The primary goal is to maximize crop yield while minimizing the use of resources like water and land. Indoor farming is not only sustainable but also offers numerous benefits, including year-round production, reduced transportation costs, and the ability to grow crops in urban areas where space is limited.
The Benefits of Indoor Farming
Indoor farming offers a plethora of advantages that make it an attractive option for both small-scale and large-scale agricultural operations. One of the most significant benefits is the ability to control the growing environment. By regulating factors such as temperature, humidity, and light, farmers can optimize conditions for plant growth, leading to higher yields and better-quality produce. Additionally, indoor farming reduces the need for pesticides and herbicides, as the controlled environment minimizes the risk of pests and diseases.
Another major advantage is the reduced water usage. Traditional farming methods often require large amounts of water, which can be a significant strain on resources, especially in arid regions. Indoor farming, on the other hand, uses advanced irrigation systems that deliver water directly to the roots of the plants, reducing waste and conserving water. This not only makes indoor farming more sustainable but also more cost-effective in the long run.
Economic and Environmental Impact
The economic impact of indoor farming is substantial. By growing crops closer to urban centers, farmers can reduce transportation costs and ensure fresher produce for consumers. This also creates new job opportunities in urban areas, contributing to local economic development. From an environmental perspective, indoor farming helps reduce the carbon footprint associated with traditional agriculture. By minimizing the need for land clearing and reducing water usage, indoor farming contributes to the preservation of natural resources and the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Popular Indoor Farming Techniques
There are several techniques used in indoor farming, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. Hydroponics, for example, involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution without the use of soil. This method is highly efficient and allows for precise control over nutrient levels, leading to faster growth and higher yields. Aeroponics, on the other hand, involves growing plants in an air or mist environment without the use of soil or an aggregate medium. This technique is particularly effective for propagating plants and can lead to rapid root development.
Aquaponics is another popular technique that combines aquaculture (raising aquatic animals such as fish) with hydroponics. In this system, the waste produced by the aquatic animals provides nutrients for the plants, while the plants help to purify the water. This symbiotic relationship creates a sustainable and efficient farming system that can produce both fish and crops. For those interested in chia seed indoor farming techniques, exploring these methods can provide valuable insights into optimizing growth and yield.
Choosing the Right Technique
Choosing the right indoor farming technique depends on several factors, including the type of crops being grown, the available space, and the resources at hand. For example, hydroponics is well-suited for growing leafy greens and herbs, while aeroponics is ideal for propagating plants. Aquaponics, on the other hand, is a versatile technique that can be used to grow a wide variety of crops, including fruits, vegetables, and even flowers. It is essential to research and understand the specific requirements of each technique to make an informed decision.
Getting Started with Indoor Farming
Starting an indoor farming operation can be a rewarding endeavor, but it requires careful planning and preparation. The first step is to choose the right location. Ideally, the space should have access to natural light and be well-ventilated. If natural light is limited, artificial grow lights can be used to supplement the lighting. The next step is to select the appropriate growing system. This will depend on the type of crops being grown and the available resources. Once the system is in place, it is essential to monitor and maintain the growing environment to ensure optimal conditions for plant growth.
Investing in high-quality seeds and nutrients is also crucial. High-quality seeds ensure healthy and robust plants, while high-quality nutrients provide the essential elements needed for growth. Regular monitoring and maintenance of the growing system are also essential to prevent issues such as pest infestations and nutrient deficiencies. By following these steps, beginners can set themselves up for success in the world of indoor farming.
Challenges and Solutions in Indoor Farming
While indoor farming offers numerous benefits, it also comes with its own set of challenges. One of the most significant challenges is the high initial investment required to set up an indoor farming operation. The cost of equipment, such as grow lights, irrigation systems, and environmental control systems, can be substantial. However, the long-term benefits, such as reduced water usage and higher yields, can offset these initial costs.
Another challenge is the need for specialized knowledge and skills. Indoor farming requires a deep understanding of plant physiology, nutrient management, and environmental control. Fortunately, there are numerous resources available, including online courses, workshops, and mentorship programs, that can help beginners acquire the necessary skills and knowledge. By investing in education and training, aspiring indoor farmers can overcome these challenges and achieve success in their endeavors.
Overcoming Space Limitations
Space limitations can be a significant challenge, especially for those living in urban areas. However, there are several strategies that can be employed to maximize the use of available space. Vertical farming, for example, involves growing crops in stacked layers, allowing for higher yields in a smaller footprint. This technique is particularly effective for growing leafy greens and herbs. Additionally, using compact growing systems, such as hydroponic towers and aeroponic systems, can help maximize space utilization and increase productivity.